Feeding Intolerances
-
Treat nausea and vomiting by using the tips below. Contact your doctor if symptoms persist.
Begin feeding at a slower rate, then increase the rate gradually over 24-48 hours.
Ensure the formula is not spoiled or contaminated.
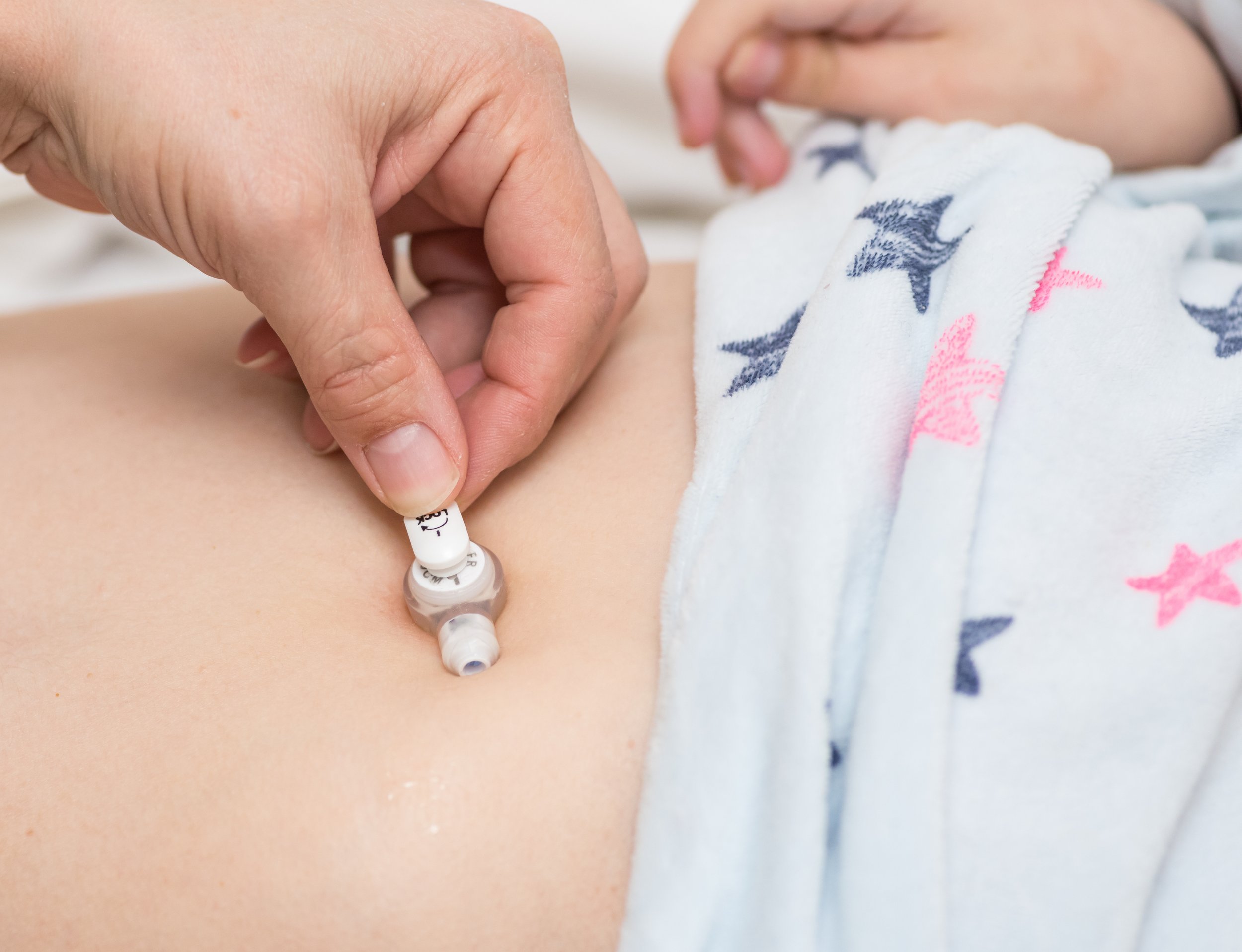
Confirm tube placement before feeding.
Ensure your child’s head is elevated (minimum 30 degrees) during the feeding and for at least 30 minutes after the feeding.
Make sure the formula has reached room temperature before administering.
Check any medications for possible side effects related to abdominal pain.
-
Treat constipation by using the tips below.
Confirm your child’s daily water intake.
Check any medications for possible side effects related to bloating and constipation.
Talk to your doctor about changing the formula to one with more fiber.
-
Treat diarrhea by using the tips below. If diarrhea occurs for more than 24 hours, contact your doctor.
Check any medications for possible side effects related to bloating and constipation.
Talk to your doctor about changing the formula.
Ask your doctor about formula with specialized ingredients to support absorption and tolerance.
-
Bloating can occur after feeding or overfeeding and cause discomfort and/or gas. Your child’s stomach may look swollen or be hard to the touch. If this occurs, try venting the G-tube:
Attach a 60 ml open (with the plunger removed) syringe to the feeding tube or extension set, if your child has a button.
Pour a little water into the syringe and hold the syringe below your child’s stomach, then unclamp the tube or extension set to let the air escape. The water should bubble.
After the air escapes, let any stomach contents/formula slowly go back into the stomach.
Lastly, re-clamp the feeding tube or take off the button extension set.
G-tube Site Complications
-

Granulated Tissue
Shiny red tissue that builds up around the G-tube site is called granulated tissue. The G-tube site may easily ooze and/or bleed. A small amount of tissue is normal, but if the tissue is painful and excessive, call your doctor.
-

Skin Irritation
Skin irritation is common and is most likely from leaking. Leaking contents include stomach acid which can burn the skin. Treat skin irritation using the leaking/drainage tips below.
-

Leaking/Drainage
A small amount of leaking and drainage (yellow, green, brown) around the stoma site is normal. Be sure to clean properly and remove all crusted drainage. If the leaking is persistent and does not improve, call your doctor.
-
• Confirm the placement of the tube.
• Administer feedings and medications slowly.
• Ensure proper cleaning and drying of the stoma site.
• Confirm and monitor the amount of water in the balloon.
• Dressings are not required unless your child is likely to pull the tube. Never place dressings under the bumper; this places unnecessary pressure on the gastrostomy site.
